Reviewed by Brian St. Pierre, MS, RD and Helen Kollias, PhD
It’s like my thoughts were under a pile of garbage.
On a Friday night, as my husband and I tried to figure out where to eat, a typical conversation would go like this:
Me: Do you want to go to that restaurant?
Him: What restaurant?
Me: I can’t think of the name. We’ve eaten there before. It’s that place with the peanut shells on the floor? It’s next to… You know… It’s on that road where we used to take the dog to the vet. Do you know the one I’m talking about??
It was as if certain details got lost in a pile of sludge in the deep recesses of my brain. Then, hours later, the details would escape, and I’d shout into an empty room…
“Texas Roadhouse!”
Sludginess with proper nouns is typical for people who are middle-aged and beyond.
However, what seemed to be happening to me, increasingly in my late 40s and early 50s, felt far from typical.
Not only could I never seem to spit out the names of various restaurants or people or books or movies or so many other things, but my brain was also pooping out during the workday.
I’d sit in front of my computer screen, stare at a document, and will myself to do something constructive with my fingertips. Everything seemed hazy, like those first few moments in the morning when you’re awake enough to turn off the alarm but too sleepy to do basic math.
I had my good moments, usually in the morning, when I attempted to pack eight hours of writing into the two or three hours I possessed mental clarity.
On my worst days, however, I awoke with a haze I never managed to shake. Work was a non-starter. Nor did I have enough bandwidth to read, or do much of anything, really.
I sought medical advice.
Three healthcare professionals recommended antidepressants. I tried one, and felt even worse. I tried another. I tried yet another at a higher dose. Still, I felt like a zombie. Another professional gave me a sleeping pill. It left me feeling even more drugged.
Someone tested my thyroid. There was nothing wrong with it. Nor was I anemic. I tried supplements, mushroom coffee, and just about any product with the word “think” somewhere on its label.
Finally, after nearly two years of seeing a revolving door of doctors, I made an appointment with a gynecologist for my yearly exam. I mentioned vaginal dryness. That information triggered her to ask a string of questions that had nothing to do with my undercarriage. How was my sleep? Mood? Energy levels? Was I experiencing hot flashes? How about brain fog?
“Funny you should mention brain fog,” I said in my usual hazy monotone. “I feel like I’m barely alive.”
By the end of the visit, I understood that I’d likely never had depression.
What I “had” was menopause.
My gynecologist sent me home with prescriptions for estradiol and progesterone.
Within days, it was as if someone had flipped a switch.
I could think again. I could type words again. I could follow conversations. I could work past noon.
And, for the first time in years, I could sleep more than two hours without waking.
Now, menopause isn’t a medical condition.
Nor is it a disease.
Instead, like puberty, it’s a life stage—a transitional moment to be precise.
Once you’ve gone 12 consecutive months without a period, you’ve reached menopause. And from that moment onwards, you’re officially “postmenopausal.”
As women approach this transitional moment, hormone levels fluctuate and fall, triggering dozens of symptoms. Weight gain and reduced sex drive get a lot of attention.
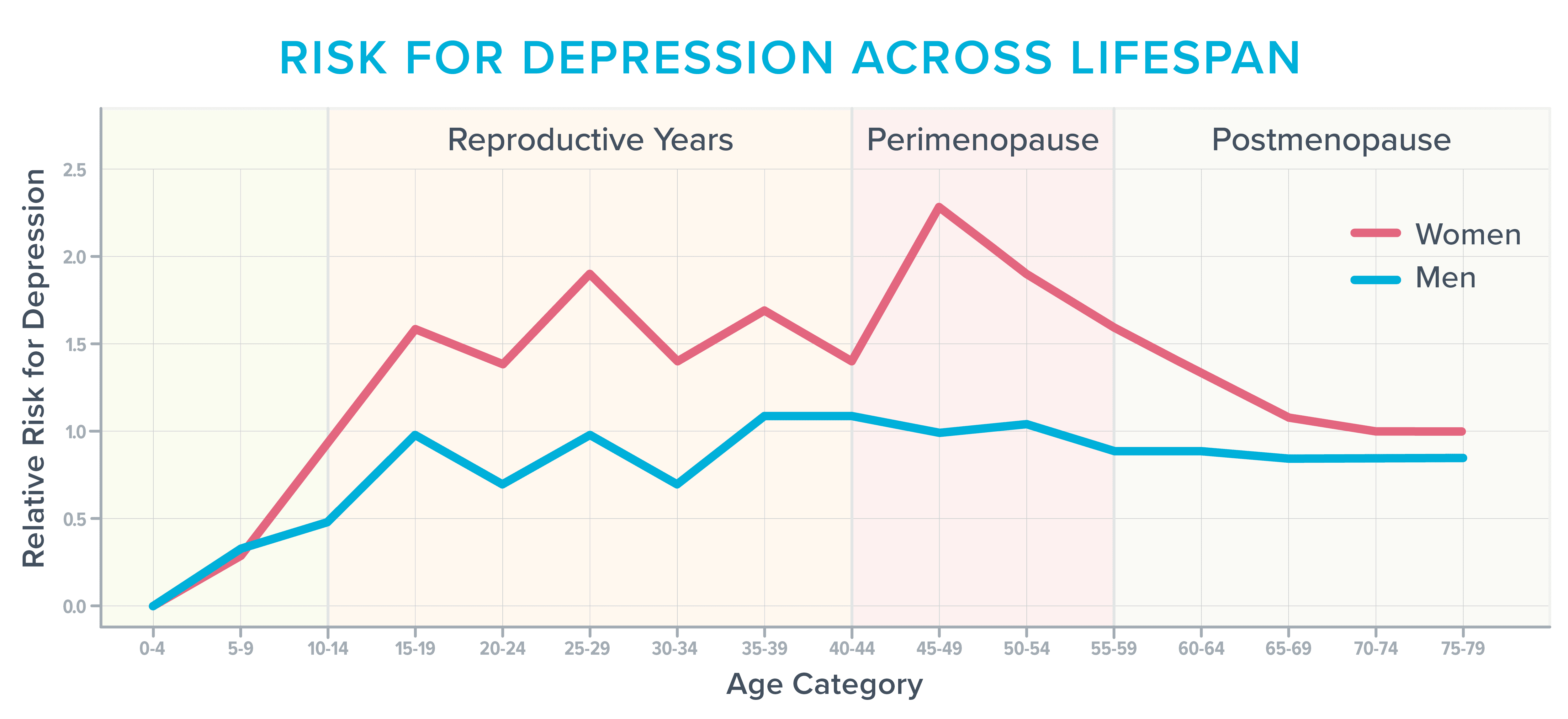
However, during and after menopause, roughly 40 percent of women report increased irritability, mood swings, anxiety, fatigue, and trouble concentrating, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.1 2 As the following image shows, it’s also one of the most vulnerable times in a woman’s life to develop depression,3 particularly if they’ve struggled in the past with it before.
Before starting hormones, I often found myself sobbing for no reason. Other times, the world’s stimuli felt too… stimulating.
Normal everyday sounds—like the buzz of traffic or people at the mall—literally hurt. I was jumpy and irritable and felt anxious about situations that had never bothered me in the past, such as driving over bridges or through construction.
It’s not completely clear what drives these cognitive and emotional symptoms.
Fluctuating hormone levels likely play a role, as do typical age-related changes in the brain.
In addition, during this stage of life, women often deal with several issues that siphon cognitive capacity faster than a thirsty vampire drains a carotid.
During their 40s and 50s, for example, many women have reached the peak of their careers, with responsibilities that follow them home and keep them up at night. They may also be parenting angst-filled teens, caring for aging parents, adjusting to an empty nest, questioning their marriage, or trying to wrap their bank account around the latest statement from the college bursar or hospital billing department.
However, one of the lesser-known and talked about triggers for cognitive discontent has nothing to do with aging or life stress and everything to do with that hallmark menopausal symptom: the hot flash.
Anatomy of a hot flash
Hot flashes, which happen during the day, and night sweats, which occur at night, fall under the category of vasomotor symptoms. (The word “vasomotor” refers to the constriction or dilation of blood vessels which, in turn, can influence everything from blood pressure to sweating.)
During a hot flash or night sweat, norepinephrine and cortisol levels rise. Blood vessels dilate in an attempt to shed heat. Blood pressure and heart rate increase.
Depending on the severity of the hot flash, your skin might redden as sensations of warmth spread through your face, neck, and chest.
You might sweat, experience heart palpitations, or feel anxious, tired, or faint.4
It’s not entirely clear why hot flashes crop up around menopause.
According to one theory, falling estrogen levels affect the hypothalamus, the area of the brain involved in temperature regulation. The brain’s internal thermostat gets wonky and occasionally thinks your body is too hot or cold (when it’s not).
How vasomotor symptoms change the brain
For many years, experts thought of vasomotor symptoms as mere inconveniences or sources of embarrassment.
(To be honest, so did I. During all of those fruitless visits to various healthcare professionals, it never occurred to me to mention them.)
However, an increasing body of research has revealed that hot flashes may do more than make us uncomfortable or force us to change our sheets in the middle of the night.
They may also affect our blood vessels and brains—and not for the better.5 For this reason, an increasing number of experts now consider vasomotor symptoms to be a treatable medical condition.6 7 8
Hot flashes and brain lesions
In one study, researchers asked 226 women to wear monitors that tracked when they were experiencing a hot flash. The women also underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), filled out sleep diaries, and wore smartwatches that recorded how often they woke at night.9
As researchers looked at the brain images obtained from women who experienced the most hot flashes, they noticed an abundance of patchy areas called whole-brain white matter intensities.
These lesions were once thought of as a typical consequence of aging. However, neuroscientists now believe that the presence of whole-brain white matter intensities is predictive of future cognitive decline.
People with an abundance of these brain lesions are twice as likely to get diagnosed with dementia and three times as likely to have a future stroke.10
The blood vessel connection
It’s thought that the increased presence of whole-brain white matter intensities may stem, in part, from changes taking place in the blood vessels that feed the brain.
A three-year study of 492 women supports that theory. It determined that women who experienced frequent hot flashes also tended to experience unhealthy changes in their blood vessels, such as an inability to dilate to accommodate increased blood flow.11
Other research has linked frequent hot flashes with increases in the following:
- Thickening in the carotid arteries that supply blood to the brain, face, and neck12
- Body fat
- Total and LDL cholesterol
- Insulin resistance13 14 15 16
The sleep connection
In addition to directly affecting the blood vessels, frequent hot flashes may also affect the brain by disturbing sleep.17
Interestingly, many women don’t necessarily know that hot flashes are disturbing their sleep.
They may instead—as I did—assume they have insomnia or sleep apnea.
That’s because night sweats aren’t always sweaty.
By the time a surge in cortisol and norepinephrine jolts a woman awake, the hotness of the flash may have dissipated. So, it can feel as if she’s repeatedly waking, over and over and over again, for no discernable reason.
These frequent awakenings may interfere with the brain’s ability to consolidate memories, metabolize toxins, and store all the names, dates, and facts one encounters daily.
It can also lead to lost connectivity in the hippocampus, a part of the brain that’s important for learning and memory.
Sleep loss also means the amygdala, a part of the brain involved in emotion, becomes more reactive, causing people to feel more easily stressed, anxious, irritable, frustrated, or enraged.18 19
All of these brain changes can set in after just days to a week of lost sleep. So, imagine what happens when you’ve been waking over and over again—for years.
Why it can be hard to get help
To diagnose depression, healthcare professionals use a tool called the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) depression scale. If you check off four of the nine symptoms on the scale, you’re considered depressed.
However, four of the symptoms on the checklist also overlap with the symptoms of menopause-related sleep deprivation:
- Little interest or pleasure in doing things
- Trouble falling or staying asleep
- Feeling tired or having little energy
- Trouble concentrating on things, such as reading the newspaper or watching television
Check off those four items, and you might be diagnosed with depression, even if what’s really ailing you is the battle with sleep you’ve been waging since you turned 47.
A lack of menopause-specific training
Another problem: On surveys, 80 percent of medical residents admit they feel “barely comfortable” talking about menopause.20 In addition, few residency programs—including ob-gyn residency programs—offer training in it.21
Given the above, it’s no wonder so many healthcare professionals never think to ask about hot flashes or sleep disturbances when people like me show up complaining of fatigue, lack of gumption, and an inability to focus.
In addition, even when it’s clear that vasomotor symptoms are leading to cognitive and emotional symptoms, many healthcare professionals still shy away from prescribing menopausal hormone therapy (also called hormone replacement therapy, or HRT), often telling women that supplemental hormones are “not safe” or “too risky.”
These professionals are practicing what Michigan-based menopause-trained gynecologist Jerrold H. Weinberg, MD, calls “defensive medicine.”
“It’s one of the first reflexes doctors have when they recommend a treatment,” says Dr. Weinberg. “They worry they’re going to get sued.”
What the research actually says about hormone therapy
These worries are based on research done several decades ago that linked the use of certain types of hormones with a slightly increased risk of developing breast cancer or stroke.22
However, according to more recent research, that small increased risk seems to depend on several other factors, such as age, dose, the type of hormonal preparation, and the duration of hormone use.23 24
As long as you’re younger than 60 and have been postmenopausal for fewer than 10 years, many experts now say the benefits outweigh the risks for women with moderate to severe menopausal symptoms.25
It’s also counterbalanced by health benefits such as reduced risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease or osteoporosis, says Dr. Weinberg, who confirms the health benefits of menopause hormone therapy far outweigh the risks for most women.
Because some antidepressants can lift mood, improve sleep, and reduce hot flashes, some healthcare professionals turn to them instead of menopause hormone therapy. As with any medicine, antidepressants have their own list of side effects. However, for someone practicing defensive medicine, they often seem like a safer bet, says Dr. Weinberg.26 27 28
How to advocate for your health
If you or your client are on what seems like a never-ending quest to find a healthcare professional who understands menopause, use the following advice from Dr. Weinberg and Helen Kollias, PhD, an expert on physiology and molecular biology and science advisor at Precision Nutrition and Girls Gone Strong.
▶ Seek care from a menopause-trained health professional.
Usually, these professionals list this training and interest in their bio. For example, they might list “menopause” as an area of focus.
You can also search this database for practitioners who have earned a certification from the Menopause Society.
▶ Document your symptoms.
Write them down. That way, if you feel foggy or nervous during your appointment, you can lean on your notes.
This information can also help you judge whether MHT or another medicine is working. Based on your symptom data, you and your healthcare professional may decide to switch to a different medicine or change your dose.
Consider tracking:
- How often you get hot flashes
- The number of hours in a typical day you find yourself battling brain fog
- How often you experience fatigue, anxiety, rage, or some other symptom
- How often you wake up at night
▶ Be as specific as you can during your appointment.
Saying something like “I don’t sleep well,” is less likely to get you the right kind of help than saying, “During the past seven days, I’ve only gotten four uninterrupted hours once. I wake, on average, five times a night. On a typical night, my longest stretch of sleep is three hours.”
If you use a smartwatch, come ready to fire up your health app, so your healthcare professional can see the data.
▶ Talk about the pros and cons of treatment.
There’s a concept in medicine known as “shared decision-making.” Part of that process involves frank discussions about the benefits and risks of a given treatment. Then, patients and clinicians work together to make decisions based on those benefits and risks.
Many healthcare networks encourage clinicians to use shared decision-making, as it seems to reduce patient complaints as well as malpractice lawsuits.29 30
For this reason, shared decision-making can help shift a healthcare professional out of the “defensive medicine” mindset.
You might ask questions like:
- “I’m interested in seeing if menopausal hormone therapy might be helpful. Could we discuss if I’m a good candidate?”
- “I’ve read that menopausal hormone therapy could slightly increase my risk of breast cancer. Could you help me understand my personal breast cancer risk based on my family history, age, body weight, and lifestyle?”
- “Osteoporosis runs in my family, as does dementia. I’ve heard that menopausal hormone therapy might help to reduce the risk for both, in addition to helping me sleep. Could you help me weigh the pros and cons?”
How to improve mental and emotional health during menopause: 9 lifestyle strategies
The lifestyle habits that improve mental and emotional health during menopause aren’t terribly different from the lifestyle habits that improve overall health—for any person, at any stage of life.
Other than avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and spicy or hot foods, there’s no special diet for people with vasomotor symptoms. (And by the way, tofu and other soy products don’t seem to help with vasomotor symptoms as much as once thought30—though they’re still nutritious.)
Strategy #1: Lean into fundamental health strategies.
Healthy behaviors don’t necessarily change during middle age.
Nutrition, physical activity, stress management, sleep, social connectedness, and a sense of purpose matter just as much during the menopausal transition as they do when we’re younger. However, these fundamentals are even more important to dial in as life progresses.
So consider:
- Are you setting aside enough time for sleep and rest?
- Are you physically active?
- Are you eating a diet that’s mostly minimally processed and full of brightly colored produce, healthy fats, lean protein, fibrous vegetables, and legumes?
- Do you regularly connect with other humans in ways that help you buffer stress and feel supported?
- Do you find ways to experience awe, joy, curiosity, peace, and purpose?
If you answered “no” to some or all of those questions, consider why that is. What’s stopping you? How might you remove barriers or shore up support to make those fundamentals easier?
Strategy #2: Experiment with creatine.
In addition to helping to blunt age- and hormone-related losses in muscle and bone mass, creatine may also help bolster mood and brain function while reducing mental fatigue.
It also seems to counter some of the negative effects of sleep deprivation. 32 33 Research shows a daily dose of 5 to 7 grams of creatine monohydrate is effective.
Strategy #3: Get regular about light exposure.
In addition to helping you feel alert, sunlight helps to set the internal clock in your brain that makes you sleepy at night and spunky in the morning. Morning and late afternoon light exposure seem particularly potent.
In a study of 103 people, exposure to morning sunlight predicted better sleep quality the following night. When people spent time outdoors in the mornings, they fell asleep more quickly, slept longer, and experienced fewer awakenings the following evening.34
Sunlight may also improve mood and concentration.35
Strategy #4: Go easier at the gym.
If you’re already worn out, long, intense exercise sessions will likely make you feel worse.
For one, injuries crop up much more easily at middle age than during our 20s and 30s. In addition, it takes longer to recover between sessions.36
String too many overly zealous workouts too close together, and you’ll not only likely start to feel achy but also more irritable, tense, and tired.
However, much like a cold shower, short bursts of exercise may help you to feel alert during the day.
If you’re falling asleep at your desk, encourage yourself to take short movement breaks such as a 5- or 10-minute walk outdoors or a quick set of pushups or squats.
In addition, you may find gentle exercise—such as yoga or stretching—helps you relax before bed. Just don’t make it too intense, or you’ll trigger a release of adrenaline.
Whenever you exercise, tune into how your body feels, especially after a particularly bad night of sleep.
We’re not saying you should never exercise vigorously or try to beat your lifting PRs. However, depending on your sleep and recovery, you might want to pare things back, especially if you’ve traditionally hit the gym hard.
You can still do intense sessions—just balance them out with more moderate sessions, as well as proportionate recovery.
Depending on how you feel, you might decide to go all out, as usual.
However, you might also decide to do a zone 2 training session instead of an intense run. Or, if you’re resistance training, you might still do your planned session, but reduce the number of sets, reps, or volume lifted.
Strategy #5: Investigate Cognitive Behavior Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I).
This research-based therapy for insomnia can help you develop skills and mental reframes that encourage sound sleep.
For example, a CBT-I therapist will help you develop the skill of getting up at the same time every day, regardless of how badly you slept (or didn’t sleep) the night before.
(Read more: Three CBT-I skills that can transform how you sleep.)
Strategy #6: Get real about stress.
You may not have the energy (or desire) to do everything you did when you were younger. (When you were 36, your daily checklist defied time and space.)
As a result, you might benefit from looking critically at your current responsibilities to see which ones you can shrink or downsize. For several days, track how you spend your time and bandwidth. Then, analyze your data.
Ask yourself:
- Is this how you truly want to spend your time and energy?
- Does your current schedule allow you to rest, recover, and tend to your own needs? Or, do you spend nearly all of your time and energy caring for and providing for others?
- What changes could you make to prioritize rest and recovery?
If you’re a coach, use the Wheel of Stress Assessment to help clients identify different dimensions of their life that might be draining their mental and emotional capacity. (When you know specifically where your stress is coming from, you have a better chance of resolving it.)
If it’s demands from other people that prevent you from prioritizing self-care and recovery, you might like to read: How saying “no” can seriously change your life.
Strategy #7: Experiment with cooling technology.
You might find you sleep better and experience fewer night sweats if you sleep in a cooler environment.
Try turning down the thermostat a couple of degrees, using a fan, or investing in an electric cooling mattress pad.
Strategy #8: Take frequent breaks.
When you feel the fog take over your brain, it’s not likely you’ll be doing “your best work” anyway.
So, for a block of time—say, 20 minutes—permit yourself to do nothing. You might:
- Relax with a cold beverage
- Cuddle with a pet
- Gaze out a window
- Sit outdoors while listening to the birds
- Call a friend
If you need a quick “refresh,” you can also try a 5-minute mind-body scan.
Get your body into a comfortable position. For example, you might use the yoga “legs up the wall” pose or lie down and place a pillow under your knees.
Then, close your eyes and bring your attention to physical sensations in your body. Start at your head, and work your way down to your toes.
Don’t judge or rush to change anything. Just observe, like a scientist. You can also scan your mind, for example, by noticing thoughts.
When you’ve completed the scan, consider:
- What are you feeling physically?
- What are you feeling emotionally?
- What are you thinking?
You don’t have to “do” anything with the information you uncover, just notice.
Strategy #9: Follow a diet that promotes healthy circulation.
The foods that protect the blood vessels around your heart can also protect the blood vessels in your brain.
For example, both the MIND and Mediterranean diets are associated with a reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease and depression.37 38 These eating patterns are rich in vegetables, fruit, whole grains, olives, beans, fish, and other minimally-processed whole foods.
In addition, nitrate-rich foods like beets and dark, leafy greens may help to dilate blood vessels, temporarily improving memory by helping more blood to reach the brain.39 40
(For more on how our diet can support brain function and emotional regulation, read: Nutrition and mental health: What (and how) to eat)
The upside of menopause
It’s frustrating when you feel like you can’t do it all.
Believe me. I know.
However, this stage of life presents a hidden opportunity, forcing you to re-evaluate what’s most important.
Before going on hormones, as my ability to type coherent words and phrases diminished, I was forced to ask an important question:
Do I really need to be doing this?
It was more of an existential question than a career-related one, and it allowed me to reassess how I wanted to spend my limited mental resources.
Given that I was self-employed, I didn’t actually need to be working eight hours a day. That was a gift, wasn’t it?
Maybe I also didn’t need to cook dinner six nights out of seven. Maybe the recipes I chose could be simplified, too.
Finally, maybe saying “no” a lot more often and without regret would allow me to continue to say yes to the things that mattered most.
Things like visiting my aging parents.
And picking up the phone whenever my kid called from college.
Or meeting a friend for a meandering walk around town.
Thanks to the hormones and life tweaks, I now have energy again. I’m also clear-headed most of the time. However, I still tend to end my work day around 3 p.m.
Why?
Because I can, and I want to.
References
Click here to view the information sources referenced in this article.

